Tunnel excavation is associated inevitably with ground loss, which, in turn, results in associated ground movement. It is, therefore, important to closely monitor the ground loss when tunnelling through urban areas.
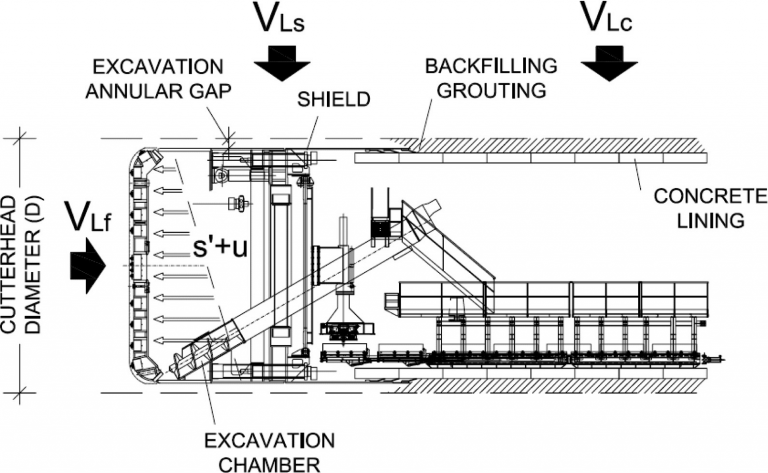
TBM excavation in an urban environment
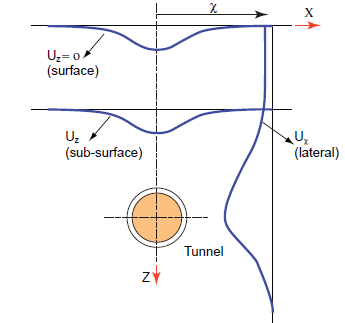
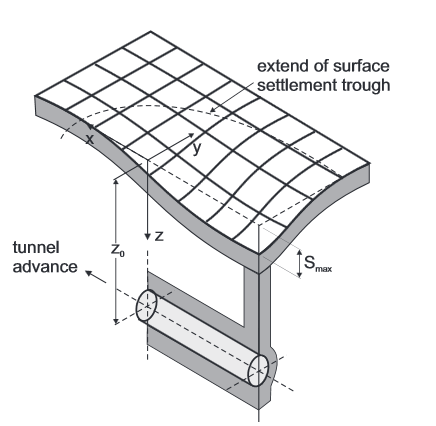
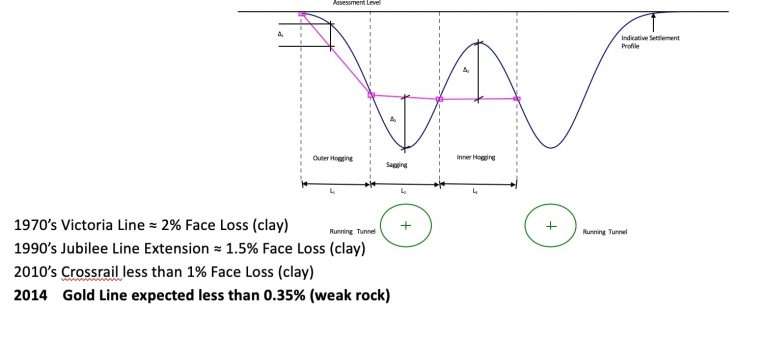
To correlate the progress of the TBM, site conditions, and topographical and geotechnical measurements is of paramount importance during tunnel monitoring in an urban environment.
There are several databases available in the market to correlate the data. One of the most advanced software is Terramove. The geotechnical database management has been used to monitor many metro projects, one of the most recent being the Gold Line in Qatar. We store the following data in the database:
- Horizontal – Vertical Alignment
- Drawings
- Pre-Construction Data
- Geological Data
- Geological Data Sheets
- Geological Profiles
- Boreholes
- Measurements of survey targets
- Geotechnical instruments
- Piezometers
- Inclinometers
- Crackmeters
- Load Cells
- Strain Gages
- Construction Data
- Work Progress (excavation, gunite, the stationing of TBM etc.)
Gold Line Metro Project is a part of Qatar Integrated Rail Project which is the key infrastructure project of Qatar National Vision 2030. Doha Metro will be one of the most advanced rail transit systems in the world when Phase I becomes operational by the end of 2019.
The east-west Gold (Historic) Line is the largest line of the project and extends from Ras Abu Aboud in the east, crosses Msheireb Major Station, and reaches Sport City in the west (near Aspire Zone). It consists of twin tunnels of an approximate length of 16 km, with ten underground stations namely Ras Abu Aboud, Qatar National Museum, Souq Waqif, Bin Mahmoud, Al Sadd, Joaan, Al Sudan, Al Waab, Sport City and Al Aziziyah.
Six TBMs were deployed to carry out ~ 32 km of tunnelling at an average depth of 20 m below ground. 24-Cross Passages and one Emergency Exit have also been constructed in the project.

Have you ever wondered how the tunnel subways are constructed and how the Gotthard Base Tunnel might have been excavated?
In this article, we will talk about:
- What is a Tunnel Boring Machine?
- What are TBMs major types?
- Micro-tunnel Shield Method
- How does a TBM work?
- Stages of TBM Construction
- Advantages of using a Tunnel Boring Machine
What is a Tunnel Boring Machine?
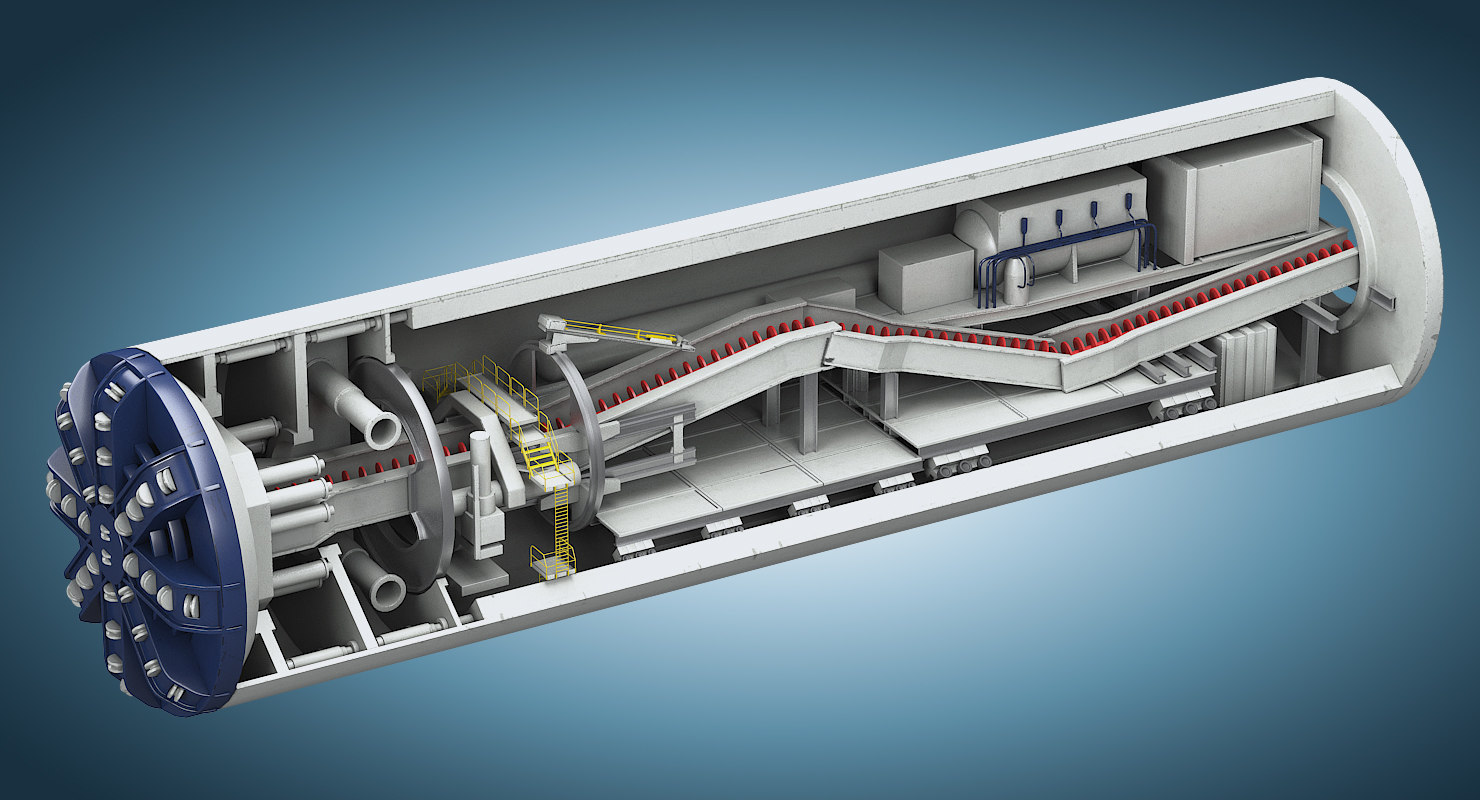
Tunnel Boring Machine(TBM) also known as a “mole”, as the name suggests is simply a machine assembled using sophisticated types of equipment for excavating tunnels with the help of a variety of soil and rock strata.
On average, a TBM excavates around 50-60 feet per day which is 20 hours of excavation approximately.
To understand how a Tunnel Boring Machine works, we will divide its components into three parts:
- Cutting Head (front)
- Tunnel Field (middle)
- Trailing Gear (rear)
Keep in mind that the type of machine to be used will always depend on the geology of the project.
Hard Rock TBMs
The Hard rock, either shielded or open-type TBMs is used to excavate rocks with the help of disc cutters which are mounted on the cutter head.
The rocks (muck) get chipped away as the disc cutter compresses stress fractures on it.
Now the excavated rocks are transferred to the belt conveyor through the cutter head openings.
These rocks are then run through multiple conveyors to get them removed from the tunnel.
Soft Ground TBMs
The Soft Ground TBMs have three main types of TBMs:
- Slurry Shield
- Earth Pressure Balance
- Open Face Type
1. Slurry Shield TBM
Slurry Shield TBMs are used when the ground conditions are granular with very high water pressure.
Hydrostatic pressure is applied on the excavation by filling the cutter head with pressurized slurry, which is also used as a transporting medium when mixed with the excavated material before it is pumped to the cutter head back and, then to a separation plant outside the tunnel.
Particles of spoil from the slurry are filtered using the Slurry separation plants to reuse it in the construction process.
2. Earth Pressure Balance TBM
It is a method of excavating, where the excavated material supports the tunnel face. It later gets plasticized with the help of slurry such that it is transportable.
We make use of the Earth Pressure Balance Machines when the soft groundwater is less than 7 bars of pressure. In this type, the cutter head not only uses disc cutter but also a combination of tungsten carbide cutting bits, drag picks and carbide disc cutters.
The spoil is then transferred into a TBM with the help of a screw conveyor also known as a “cochlea” that allows the pressure to remain balanced without any use of slurry.
3. Open Face type TBM
Open Face TBM is a method of excavating with no frontal support, relying on the fact that the ground being excavated will stand up with no support for a brief period, making it suitable to be used with rock types having strength up to 10MPa.
The cutter head excavates the face within 150mm of the edge of the shield. Now, the shield is put forward with the cutter getting rid of the remaining ground in sync with the circular shape.
Precast concrete is used to provide the ground support. Finally, Key which is the final segment expands the ring until and unless it gets tight against the circular cut of the leftover ground.
Micro-Tunnel shield method

Credit: Time Asia Group
This is a digging method which is used for small-scale tunnel constructions. The micro-tunnel boring machine is comparatively very small in size to the general tunnelling shield.
How does a TBM work?
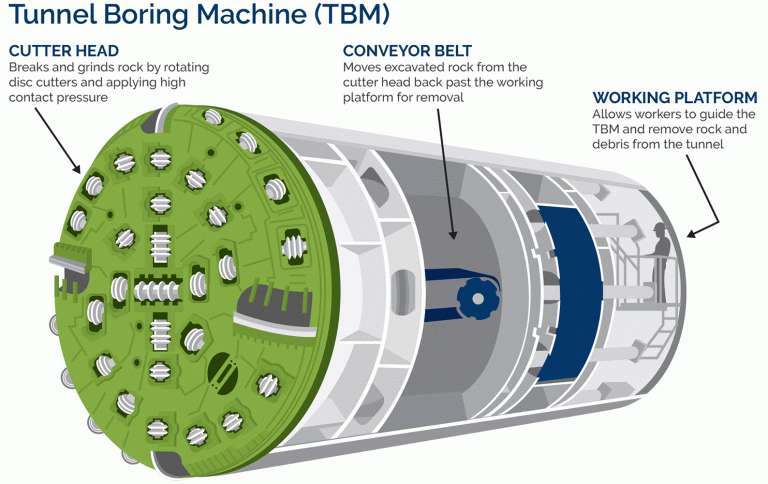
Now that we know what a TBM is, and, its types, let’s talk about how a Tunnel Boring Machine works.
The cutter head on the TBM rotates and thrusts into the rock surface that lies ahead of it. This thrust causes the cutting disc tools to break the rocks.
The grippers/braces develop the reaction to applied thrust and torque forces with the help of anchoring.
Stages of TBM Construction
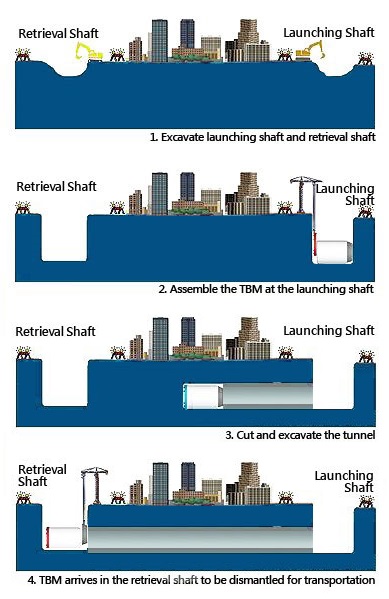
Credit: Rail system
- Excavate the launching and retrieve shaft
- Assemble the TBM at the launching shaft
- Cut and excavate the tunnel
- The TBM then arrives in the retrieval shaft and gets dismantled for transportation.
Advantages of using a Tunnel Boring Machine
- Higher advance rates: One of the significant advantages of TBM includes high advance rates or the excavation rate which is calculated based on shift time and the total distance mined.
- Continuous operations: TBM is a giant that can work continuously without any significant delay thereby, increasing the advance rate.
- Less rock damage: TBM causes less rock damage as compared to the other drilling machines that decrease the overbreak value.
- Fewer support requirements: TBM doesn’t need huge support to operate. It can operate on minimal system requirements.
Uniform muck characteristics
Greater worker safety: TBMs are safer than other machines and cause less damage to the site as well as to the people working on site.
Potential for remote, automated operation